Reference Data Sharing
In 11i/R12 there are many configuration data which ‘er shared across all the OUs. Ex: Payment term. It's good because you are required to define the data only once but the biggest disadvantage is that there is no method to restrict the access. In fusion application a new concept of data sharing is added, where you define reference data set(s) and determine how the data is shared or partitioned.
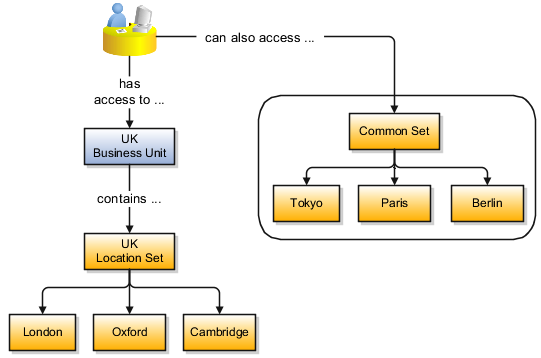
Reference data sharing facilitates sharing of configuration data such as jobs and payment terms, across organizational divisions (another new organization concept in FA) or business units. Depending on the requirement (specific or common), each business unit can maintain its data at a central location, using a set of values either specific to it or shared by other business units.
This new feature reduces duplication as well as provides the facility to restrict data as required.
From Oracle Guide
Reference data sets are logical groups of reference data that can be accessed by various transactional entities depending on the business context. Oracle Fusion Applications contains a common reference data set as well as an enterprise set that may be used as a default set. Depending on your business requirement you can create and maintain additional reference data sets, while continuing to use the common reference data set.
Ex: The senior management can decide to use a single AP payment method data set throughout the enterprise & let business unit’s managers define their own payment formats.
Partitioning
The partitioning of reference data and creation of data sets enable you to create reference entities across tables or lookup types, and share modular information and data processing options among business units. With the help of partitioning, you can choose to create separate sets and subsets for each business unit depending upon its business requirement, or create common sets or subsets to enable sharing reference data between several business units, without the need for duplicating the reference data. Partitioning provides you the flexibility to handle the reference data in a way appropriate to your business needs.
The figure illustrates the reference data sharing method (assignment to one set only, with common values) where the user can access the data assigned to a specific set in a particular business unit, as well as access the data assigned to the common set.
Tree & Tree Structure
What is a tree?
A tree is hierarchical structures that enable several data management functions such as better access control, application of business rules at various levels of hierarchies, improved query performance, and so on.
This concept is similar to the organization hierarchy in 11i & R12.
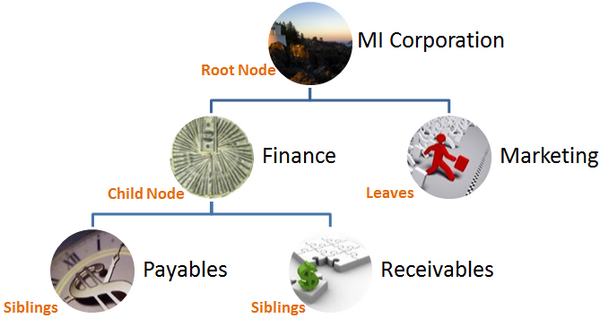
For example, MI Corporation has two departments: Marketing and Finance.
The Finance department has two functional divisions: Receivables and Payables.
Defining a tree for the MI Corporation establishes a hierarchy between the organization and its departments, and between the departments and their respective functional divisions as shown in above pic.
What is a tree Structure?
A tree structure is configuration on the basis of which trees are created. It defines and restricts the tree. A tree is an instance of the hierarchy as defined in the tree structure. Tree structures enable you to enforce business rules to which the data must adhere.
The root node is the topmost node of a tree. Child nodes report to the root node. Child nodes at the same level, which report to a common parent node, are called siblings. Leaves are details branching off from a node but not extending further down the tree hierarchy.
Important Points
- You can associate multiple data sources with a tree structure.
- Every tree structure can contain one or more trees.
- You can create tree structures specific to an application but you can share tree structures across applications.
- If you apply version control to the tree structure, it is carried over to the trees that are based on the tree structure.
- Each tree version contains at least one root node. Occasionally, a tree version may have more than one root node.
- An administrator controls the access to tree structures through a set of rules that are periodically audited for validity.
What is a tree version
A tree is created having only one version. However, users can create more than one tree version depending on the need, and they can make changes to those versions. Depending on varying requirements, users can create one or more tree versions and publish all of them or some of them by making the versions active at the same time. Similar to any other version control system, versions of trees are maintained to keep track of all the changes that a tree undergoes in its life cycle.
What are tree labels
Tree labels are short names associated with trees and tree structures and point directly to the data source. Tree labels are automatically assigned to the tree nodes. You can store labels in any table and register the label data source with the tree structure.

