iSupplier Portal
Oracle iSupplier Portal enables a buying company to communicate key procure-to-pay information with suppliers.
From Oracle data sheet
As a supplier using Oracle iSupplier Portal, you can
1.1. View and acknowledge purchase orders
1.2. Submit change requests & acknowledge purchase order change requests.
2.1. Create advance shipment notices
3.1 View receipts, view invoices and payments
4. 1.Vview inventory levels
4.2. Create work confirmation for complex work projects
As a buyer using Oracle iSupplier Portal, you can
How to Start
Before you can access Oracle iSupplier Portal:
1. Your company must be registered as a supplier to the buying company that has licensed Oracle iSupplier Portal.
2. You must be registered as an Oracle iSupplier Portal user.
Note: If you are already a supplier to the buying company and you can log into Oracle iSupplier Portal, then you and your company have already completed both of the registration tasks.
After you are registered, you can access Oracle iSupplier Portal. The tasks you perform on Oracle iSupplier Portal are determined by your current supply chain business relationship with the buying company
1. Create a user id for the supplier / site from supplier adress book.
2. Verify the user id is attached to the customer in define user form
Add the ICX_SUPPLIER_ORG_ID value as the supplier name to this user id
iSupplier Portal Setup
The only implementation prerequisite for Oracle iSupplier Portal is that Oracle Purchasing has been licensed and fully implemented.
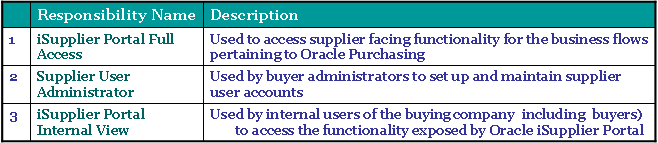
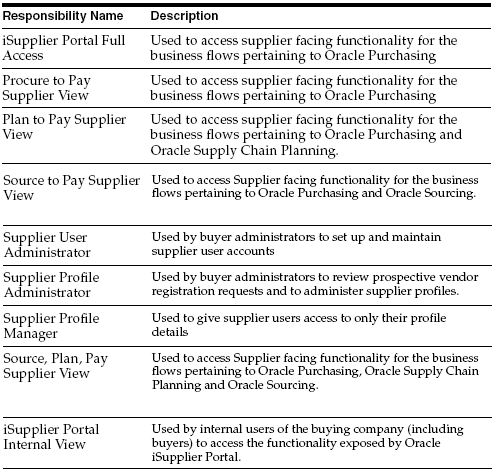
For using isupplier one needs to have the acess to the following responsibilities
Oracle iSupplier Portal is shipped with the following seeded responsibilities:The Process flowBelow diagram depicts the basic functionality of isupplier portal.
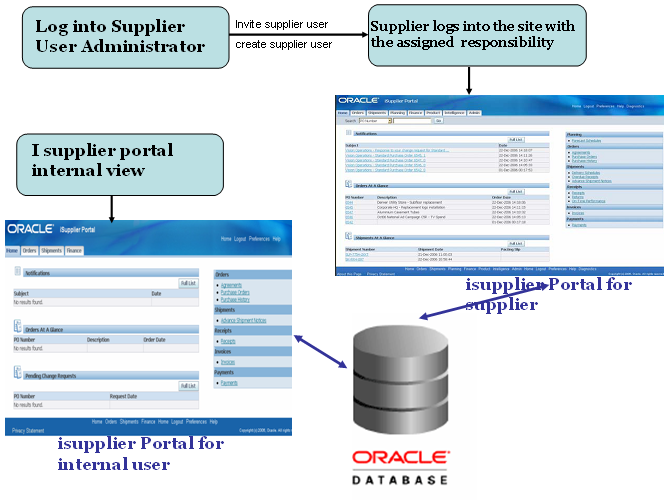
Supplier User Administrator
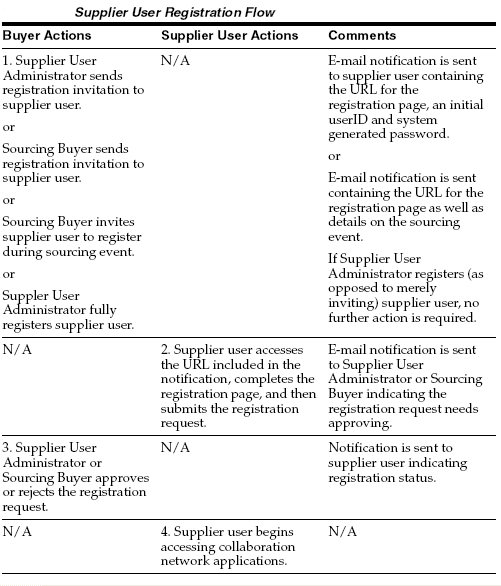
Before supplier users can access any of the collaboration network applications, a user account needs to be provided to them. Typically, user account creation is a function that system administrators perform, but the Supplier User Management(available in Supplier User Administrator/Supplier User Manegment responsibility) feature allows designated users within the buying organization to create and manage external user accounts. These designated users can register new supplier user accounts and update user details to alter the supplier users profile and access rights.
-
- Supplier User Management allows the buying teams to respond directly to the suppliers whom they are dealing with on a daily basis rather than having to process account requests through their IT department. Supplier User Management is only used to create and manage external accounts; it is not used to access and manage internal employee accounts.
-
- The registration process within Supplier User Management is the only way supplier user accounts are created. This ensures that the supplier user’s account is designated as external and is directly linked to the supplier with whom the user is associated. Supplier users can no longer be created from the User form in the regular Oracle eBusiness Suite.
- Supplier user accounts are only created for suppliers that are defined in the purchasing system.
Below disgram describes the Supplier User Registration flow.
Attribute Usage
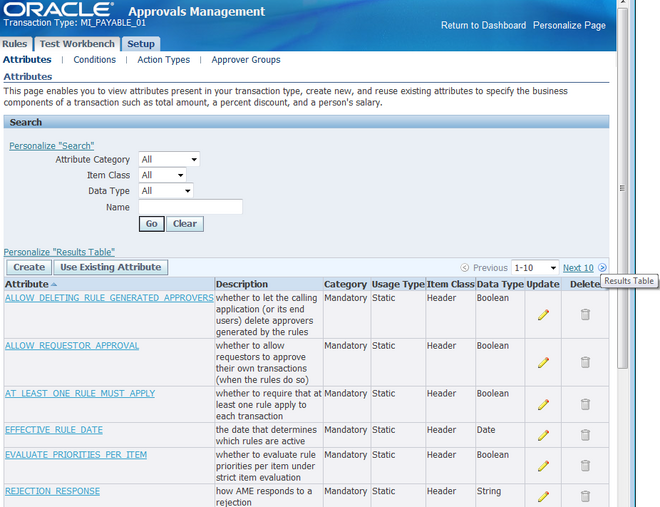 All All transaction types in AME can share an attribute name, while defining their own method of determining the attribute's value at run time as an attribute use. The ability to share an attribute's name enables several transaction types to share conditions and rules. This further enables an organization to define a single set of rules that applies to several transaction types and have a uniform approvals policy.
All All transaction types in AME can share an attribute name, while defining their own method of determining the attribute's value at run time as an attribute use. The ability to share an attribute's name enables several transaction types to share conditions and rules. This further enables an organization to define a single set of rules that applies to several transaction types and have a uniform approvals policy.
It also means that you can define an attribute name while a given transaction type may not have yet defined a use for the attribute. A transaction type only has access to conditions defined on attributes for which the transaction type has defined a use. Only users with the System
Administrator responsibility can create and edit an attribute's use.
There are two kinds of attribute use: static and dynamic.
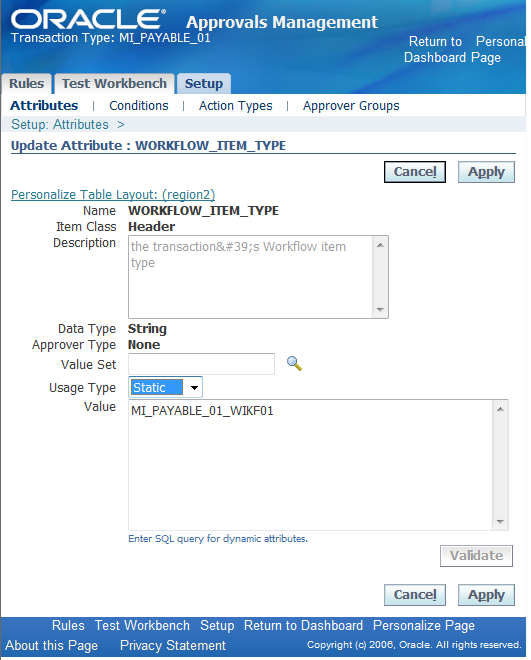
Static Attribute Use
A static attribute use assigns a constant value to an attribute, for a given transaction type. A static use always stores an attribute value as a string, regardless of the attribute's data type. It is not necessary to have a value for a static use.
A static use is common but not required for certain mandatory boolean attributes that affect how AME treats all transactions, for example, the AT_LEAST_ONE_RULE_MUST_APPLY attribute. They are similarly used for certain
required boolean attributes, for example INCLUDE_ALL_JOB_LEVEL_APPROVERS.
Dynamic Attribute Use
A dynamic attribute use assigns an SQL query to an attribute, for a given transaction type. The query must follow certain syntax rules. AME executes the query at run time to determine the attribute's value. A dynamic use is common for all attributes other than the two classes of boolean attributes described under Static Attribute Use.
A dynamic use can be up to 4000 bytes long and should not end with a semicolon. A dynamic use can reference a transaction's ID by using the bind variable ':transactionId'. A dynamic use for header-level attributes must return one row per transaction. A dynamic use for attributes belonging to subordinate-level item classes must return one
row for each item in the item class, for a given transaction. The rows must be ordered so that the ith row returned by the dynamic use is the value for the ith item ID returned by the transaction type's item-class use for the attribute's item class. Typically this means the dynamic use will include an order-by clause that references a column containing the item ID. For example, the query:
select item_quantity
from some_application_table
where transaction_id = :transaction_id
order by line_item_id
Can a dynamic attribute use reference the value of another attribute?
For example:
Attribute1: select column1 from table1
where column2 = :transactionId
Attribute2: select column3 from table2
where column4 = :Attribute1
A dynamic attribute use cannot reference other attributes' values. To implement the above example, the second attribute's dynamic use would be:
select column3 from table2 where column4 =
(select column1 from table1 where column2 = :transactionId)
AME does not allow references to attribute values within the dynamic use for two
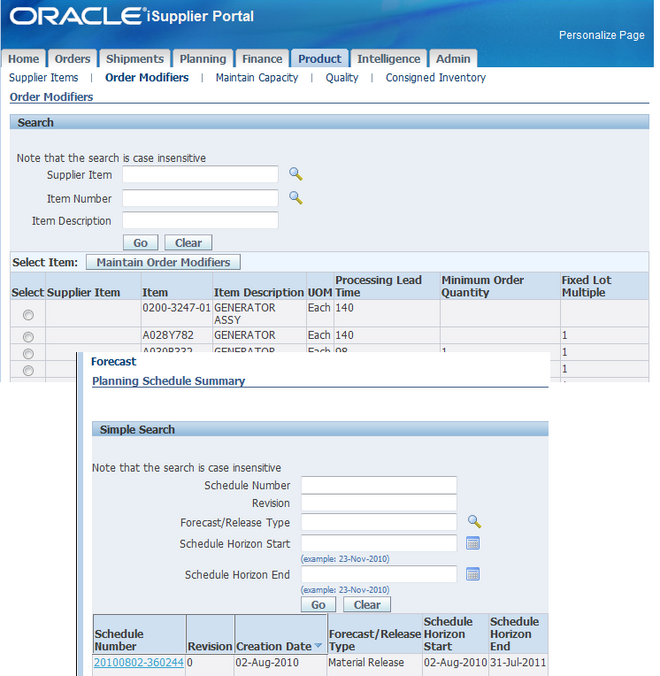
Supplier Item Summary
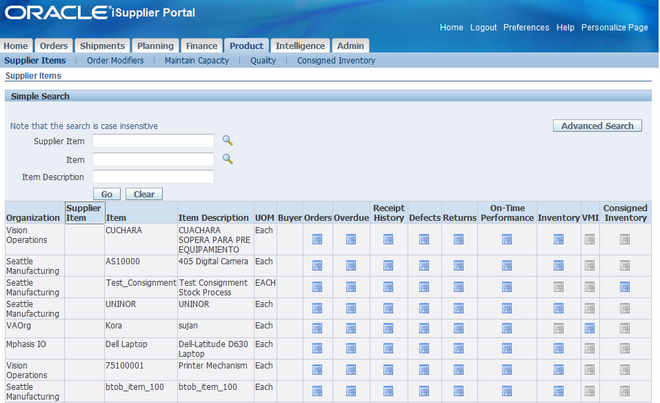
The Supplier Items page enables you to view all of the details of the products that you supply. You can view your search results in a summary format with links on each line for:
Orders
A summary of order lines placed with you for this item. This summary includes quantity ordered, quantity received, and price break information. Click PO Number, Ship-To Location, and Buyer for further information.
Overdue
A summary of overdue receipts for the selected item. Click PO Number and Receipt Number for further information.
Receipt History
A summary of receipts for the selected item. Click PO Number and Receipt Number for further information.
Defects
A summary view of failed inspection items.
Returns
A summary view of returns for an item that includes shipment information, RMA number, and quantities. Click PO Number and Receipt Number for further information.
On-Time Performance
A summary of receipts for an item that includes due dates, receipt dates, and shipping information. Click PO Number and Receipt Number for further information.
Inventory
The On-Hand page provides more details about the item, on-hand quantity, and links to both. Revision history and sub-inventory breakdown of the on-hand quantity (with locator, lot, and serial).
Vendor Managed Inventory
A summary view of vendor managed items that includes supplier, item shipment notice, and buyer information.
Consigned Inventory
A summary view of consigned items including item, shipment, and transaction information. Click the appropriate icon for further information. Most of the summaries are available to export.


 All All transaction types in AME can share an attribute name, while defining their own method of determining the attribute's value at run time as an attribute use. The ability to share an attribute's name enables several transaction types to share conditions and rules. This further enables an organization to define a single set of rules that applies to several transaction types and have a uniform approvals policy.
All All transaction types in AME can share an attribute name, while defining their own method of determining the attribute's value at run time as an attribute use. The ability to share an attribute's name enables several transaction types to share conditions and rules. This further enables an organization to define a single set of rules that applies to several transaction types and have a uniform approvals policy. 
